jo-client-platform (JOCAP)
The jo-client-platform is a 3 layer CRUD application framework for java with a ui layer based on jo-widgets.
Main goals
-
CRUD Application API
- Make it more easy to develop 3 tier enterprise CRUD applications
-
Single Sourcing
- Write applications only once for different deployments (WEB-APP, REMOTE-CLIENT, FAT-CLIENT)
-
Exchangeable data layer
- JPA and NEO4J support exists so far
Depending projects
Architecture
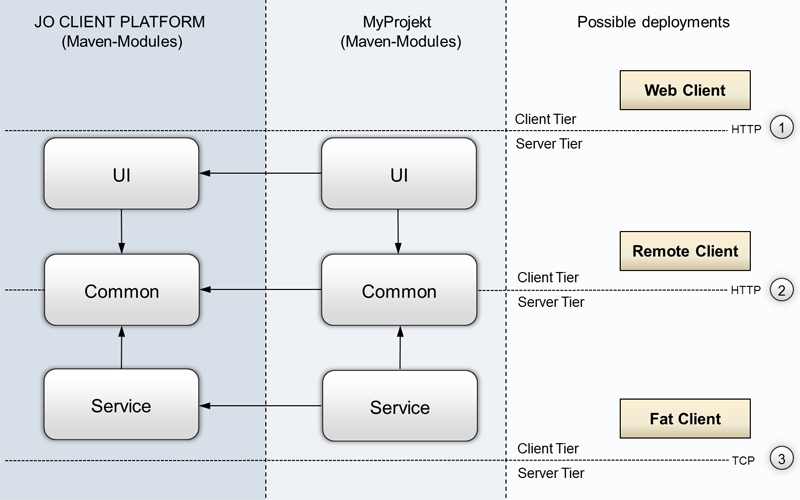
The modules of the platform are devided into UI, Service and Common. This makes it possible to deploy 3 Tier Java Desktop Applications or AJAX Webapplications based on the same businesscode.
Deployment 1 - Web Applications
By using the RWT SPI impl of jo-widgets, JOCAP applications can be deployed as AJAX WEB Applications. The UI and the Service layer will be deployed on the server tier for that.
Deployment 2 - Remote Clients
The UI layer will be deployed on the client tier, e.g. with help of webstart. The client may use one of the supported jo-widgets SPI's like Swing, SWT or JavaFX. The service layer will be deployed on the server tier, and the remoting will be done (transparent) with help of the JOCAP remoting module.
Deployment 3 - Fat Clients
For standalone applications or just for easy testing and debuging during application development, it is possible to deploy the ui layer and the service layer on the client tier.
Features
Bean Tables
- Virtual Bean Tables with millions of (virtual) rows
- Sorting and Filtering in the data layer (not in the client table)
Control Panel Provider
- Default controls for the common value types (String, Boolean, Integer, Long, Double, Short, Date, Lookups, ...)
- Different display formats (e.g. long, short, date, date_time, ...)
- Custom control panels for all attributes possible
Bean Forms
- Generic bean forms (just attributes must be defined)
- High and low level layouting
- Binding
- Validation
Bean Relations
- Visualisation of bean releations
- Modification of bean releations (link, unlink, create and link, ...)
- BeanRelationTree
- BeanReleationGraph (Graph visualization of a bean relation network)
Validation
- Bean Validation support (JSR 303)
- Custom validation support
- UI layer validation for convenience purpose
- Service layer validation for security / consistency purpose
Executions
- Executable checks (e.g. why is that button / action grey)
- BeanExecutions
- BeanDeletion
- BeanModifications
- ...
Entity Service
- Provides all informations and services for an entity id
- CRUD Services
- BeanDtoDescriptor
- EntityLinkDescriptor
Workbench
- EntityComponent (uses EntityService to create a complete master / relation / detail component)
- EntityApplicationFactory (uses EntityApplicationService to create a complete workbench application)
Services
- Asynchronous result callback
- Cancelable services
- UserQuestions to the UI layer
- Progress propagation to the UI layer
LookUps
- API to provide value sets in the UI layer
- Different display formats
- LookUpComboBox
Plugins
- Extension of the default functionality with plugins
Security
- Authorizations for all CRUD services by annotations
- Service decoration in the service layer prohibits execution
- Service decoration in the UI layer for better usability
- Expandable by custom security aspects
Exchangeable data layer
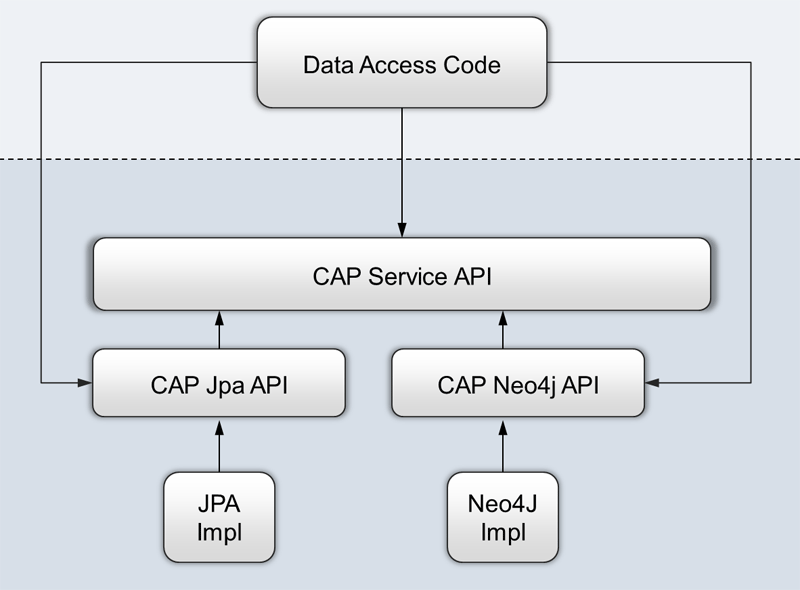
The data layer for JOCAP applications can be exchanged.
- JPA support
- Special Hibernate service decorations
- Special Oracle service decorations
- NEO4J support
- Other data layer supports possible
Third party
- No third party dependencies for the core
- Addons that uses third party code are isolated in separate modules
Common API's
Service API
The service API will be used to register and consume any kind of services. While JOCAP provides predefined CRUD services, this API can also be used independently from JOCAP. Features:
- Light weight ServiceRegistry and ServiceProvider
- Service injection with help of JavaServices, Spring, OSGi or other DI Frameworks is possible
- Generic Service ID's for easy service access (no casts needed)
- For each ServiceID there is at most one instance
- Redundant Service Resolvers can be registered
- Multiple service instances for any service interface (not Service ID)
- Injectable service decorators allow powerfull aspect weaving (e.g. remoting aspects, security aspects, ...)
Example:
IReaderService<Person> readerService = ServiceProvider.getService(ReaderServiceIds.PERSON);
Plugin API
The plugin API will be used to register and consume any kind of plugin. While JOCAP defines a lot of plugins, this API can also be used independently from JOCAP. Features:
- Light weight PluginRegistry and PluginProvider
- Plugin injection with help of JavaServices, Spring, OSGi or other DI Frameworks is possible
- Generic Plugin ID's for easy plugin access (no casts needed)
- Plugin filter with help of typed plugin properties
- Multiple plugin instances for any Plugin ID.
Security API
The security API provides a light weight API to provide:
- AuthenticationService
- AuthorizationService
- SecurityContext
The security API can be used independently from JOCAP.
Core API's
JOCAP Common API
Provides all interfaces that are used by UI and by service layer together.
Services:
- CreatorService
- LinkCreatorService
- ReaderService
- RefreshService
- LookUpService
- UpdaterService
- ExecutorService
- DeleterService
- LinkDeleterService
- EntityService
- EntityApplicationService
- AuthorizationProviderService
- PasswordChangeService
jo-client-platform service API
Provides all interfaces that are used by the service layer.
jo-client-platform ui API
Provides all interfaces that are used by the UI layer.
Widgets:
- BeanTable
- BeanTableSettingsDialog
- BeanForm
- BeanSelectionForm
- BeanRelationTree
- BeanRelationGraph
- BeanLinkPanel
- BeanLinkDialog
- BeanSelectionTable
- BeanSelectionDialog
- BeanDialog
- SingleBeanForm
- AttributeFilterControl
- LookUpComboBox
- LookUpCollectionInputField
- BeanTabFolder
- ExecutionTaskDialog
Workbench:
- EntityComponent
- EntityApplicationFactory
jo-client-platform remoting
The JOCAP remoting decorates the services of the Service API described above. Even callback parameters of services work fine, if the UI and service layer is deployed on different tiers. The JOCAP remoting can easily be injected. If the developed application only uses default services or default callback interfaces of JOCAP, it is non-essential to know all details about remoting works. Actually the application code normally has no dependencies to the remoting, but the launcher code. Nevertheless, the remoting layer stack and the involved API's will be shortly decribed here:
Remoting layers
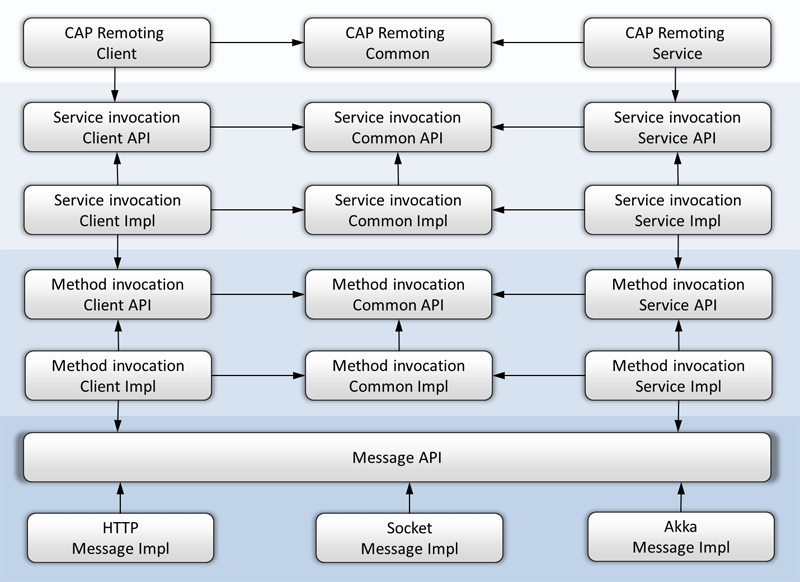
Message API
The message API is a low level API to send and receive messages with an reply channnel.
public interface IMessageReceiver {
/**
* Callback to handle a message.
*
* @param message
* @param reply channel
*/
void onMessage(Object message, IMessageChannel replyChannel);
}
It builds the base layer for the JOCAP remoting. The following implementations are available so far:
- HTTP (based on the javax.servlet API and org.apache.httpcomponents)
- AKKA (uses AKKA for the implementation)
- Socket (uses plain java sockets, not for productive use)
The messaging API can be used independently from JOCAP.
(Method) invocation API
The method invocation API allows to invoke low level methods with callback parameters. The default implementation of the invocation API uses the messaging API.The invocation API can used independently from JOCAP.
Invocation service API
The invocation service API provides an method invocation service that has an result callback parameter and interim request and response parameters. The default implementation of the invocation service API uses the invocation API.The invocation service API can used independently from JOCAP.
jo-client-platform remoting modules
The JOCAP remoting uses the invocation service API to remote the default JOCAP CRUD services and all custom services that uses the default callback parameters of JOCAP:
- IResultCallback
- IExecutionCallback
- InputStream
The remoting can even be extended for custom callback interfaces.
Screenshots
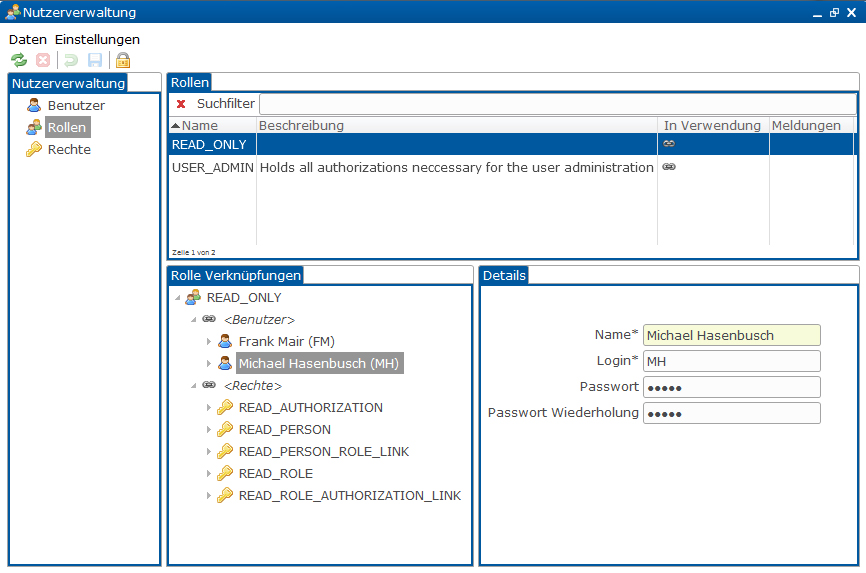
User administration based on JO CLIENT PLATFORM with Swing remoting client
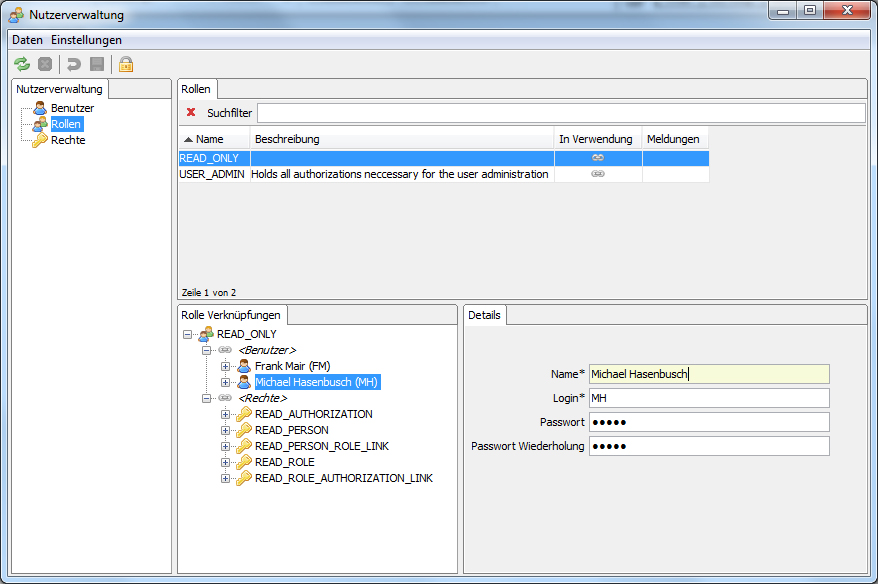
User administration based on JO CLIENT PLATFORM with SWT remoting client
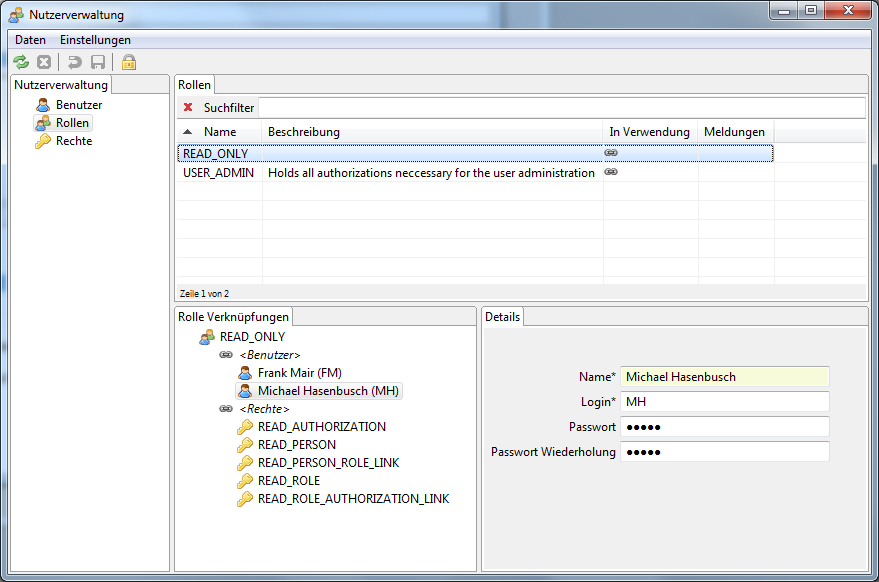
User administration based on JO CLIENT PLATFORM with RWT web client